Measuring the sustainability of an end product
To measure the sustainability of an end product, a company must not only take its composition into account, but also its use.
In many cases, a product’s greatest impact on the environment comes from the use made of that product by the customer. However, the design of the product influences the use made of it—hence the need for SMEs to design sustainable products. Seven indicators help measure the environmental impact of an end product:
- P1. Recycled/reused content
- P2. Recyclability
- P3. Renewable materials content
- P4. Non-renewable materials intensity
- P5. Restricted substances content
- P6. Energy consumption intensity
- P7. Greenhouse gas emissions intensity
These are listed on the OECD website, where additional information can be found: OECD sustainable manufacturing indicators.
Calculation of sustainability indicators for an end product
To measure these indicators, the company needs to know the proportion of recycled and reused materials, renewable materials and restricted substances contained in its products. These data can be obtained from estimates made when measuring the sustainability of production factors.
The weight of each product as well as the total volume of the products should also be known. The company should also be able to estimate the amount of energy consumed on average by its products during one year of use. It is then possible to evaluate the quantity of greenhouse gas generated by its products depending on the type of energy consumed. And lastly, the company should be able to asses the lifetime of its products, for example, by carrying out tests.
The indicators are calculated using the following formulas:
P1. Indicator (as %) of recycled/reused content of products = Weight of recycled/reused content of products / Total weight of all products
The indicator increases with sustainability
P2. Indicator (as %) of recyclability of products = Weight of recyclable content of products / Total weight of all products
The indicator increases with sustainability
P3. Indicator (as %) of renewable materials content of products = Weight of renewable materials content of products / Total weight of all products
The indicator increases with sustainability
P4. Non-renewable materials intensity over product lifetime = Weight in tons of non-renewable content of products / Expected lifetime of products in years
The indicator decreases as sustainability increases
P5. Indicator (as %) of restricted substances content of products = Weight of restricted substances content of products / Total weight of all products
The indicator decreases as sustainability increases
P6. Intensity of energy consumption of product use = (Average annual energy consumption of a product unit in megajoules x Units produced) / Standardization factor
The indicator decreases as sustainability increases
P7. Intensity of greenhouse gas emissions from products = (Average annual greenhouse gas emissions per product unit in tons of CO2 x Units produced) / Standardization factor
The indicator decreases as sustainability increases
Information relating to standardization factors is available in the section entitled “Standardization of environmental performance indicators”.
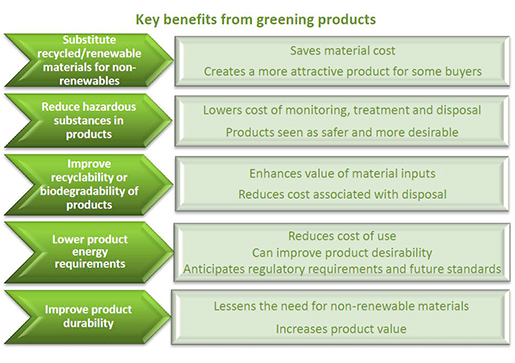
Benefits generated by improved sustainability of the end product
SMEs that pay attention to the sustainability of their end products will draw many benefits from this, including:
Source: OECD guidelines on sustainable manufacturing