Blockchain encompasses, in a secure log, digital transactions by eliminating intermediaries.
Definition and example of uses
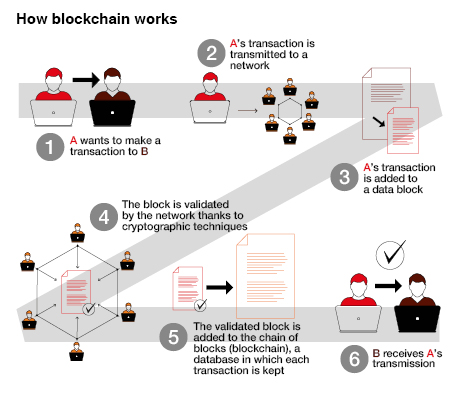
Blockchain is a sharing technology that enables the storage and transmission of information or transactions. In concrete terms, it is an account book – a digital record – containing the list of all exchanges made between users since its creation. Safe and unfalsifiable, blockchain works with a global database shared among multiple users who record all transactions between different partners.
Each user can, at any moment, using a cryptographic system, verify the validity of information, add data and record a transaction. Once included in the chain, this exchange cannot be deleted but remains open and accessible to all members. The technology thus eliminates exchange intermediaries.
The blockchain can apply to cash, stocks, votes or shares transfers. It can also be used for purposes of keeping records to ensure the traceability of an exchange. Its most famous application is the bitcoin cryptocurrency and the sharing economy like Airbnb or Uber.