For young entrepreneurs, obtaining financing for their company is a real challenge. Firstly, internal financing is not really feasible during the start-up phase of a business, either through self-financing (retention of profits) or financing through depreciation or provisions. Secondly, it is important to first establish links and a relationship of trust with banks and investors. For this reason, it is not uncommon that, during the initial creation phase of the company, at the time when they are turning their bright ideas into reality, young entrepreneurs seeking financing must turn to their family or acquaintances.
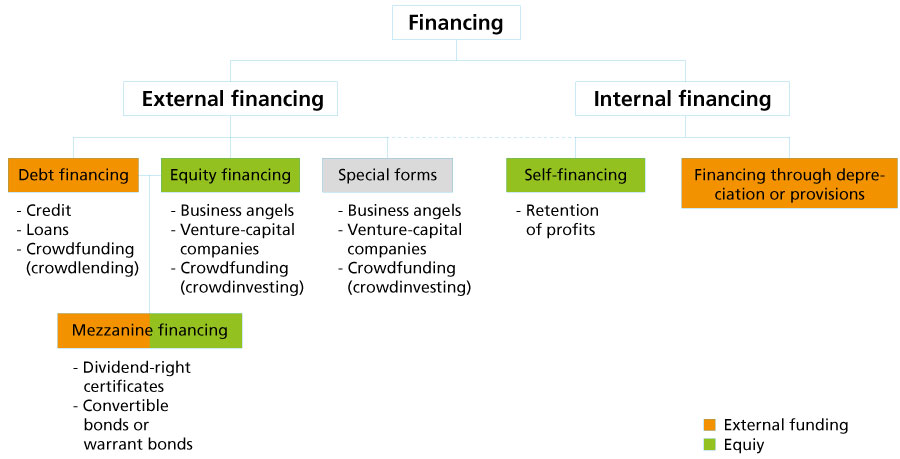
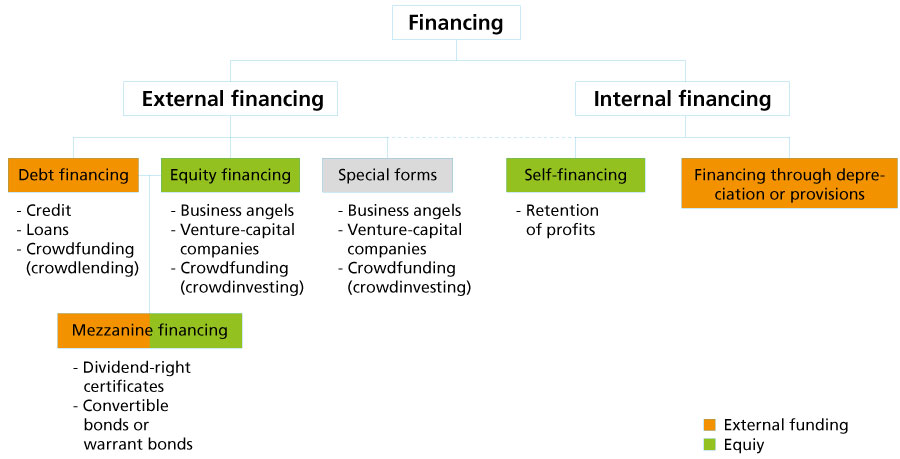
Given that an entrepreneur who has just created his or her company is generally unable to resort to internal financing, external financing is becoming increasingly important. In such cases, we differentiate between debt financing and equity financing. In addition, special forms exist such as factoring and leasing.
Debt financing
When a company resorts to debt financing, capital is loaned for a fixed period. Most frequently, this source of financing takes the form of bank credit, but it can also constitute loans granted by private individuals.
Creditors seek to minimize the risk of default as much as possible and, as a result, impose certain requirements on the borrower company. This means that when a young entrepreneur seeks to obtain financing from the bank, he or she must provide the reasons and clearly indicate the financial need. When granting credit, banks check the solvency of the company—checks that are usually based on a business plan.
Risk-adjusted pricing allows credit conditions to be tailored to the individual risk. Banks rely on the profitability of the company to assess risks based on internal rating models.
Bank credit
Crowdlending is a special form of financing through loans involving a large number of lenders. Here again, lenders expect that the borrower company wil not only repay on time the funds made available but also that it will pay them appropriate compensation on a regular basis.
Crowdlending
Equity financing
In addition to debt financing, young entrepreneurs can procure the resources they need through equity financing. Two channels exist for obtaining venture capital: business angels and venture capital companies.
Business angels
Venture capital companies
Switzerland has an open and active venture capital market which is mainly supported by foreign funds. Over the last few years, several sources have increased their investments in Switzerland significantly.
Equity financing can also, within the scope of various projects, take the form of crowdinvesting. This consists of reaching out to a large number of lenders who, in principle, each provide a small part of the total amount. As a general rule, investors are contacted through online platforms.
Crowdinvesting
Mezzanine financing
Mezzanine capital is a hybrid form combining borrowed funds and equity funds (venture capital). This form of financing lies between ordinary equity and a senior loan. To compensate for the increased risk associated with this type of operation, many mezzanine-type lenders, in addition to obtaining a fixed remuneration for their loan, contribute to the growth of the value of the company, e.g. by means of an option to purchase a given portion of the capital of the borrowing company.
Mezzanine capital
Special forms
In addition to debt financing and equity financing, companies may resort to special forms of financing.
Factoring
Leasing
Cryptocurrency fundraising (ICO / ITO)