Management system audits: are directives being respected?
Audits are part of a company’s operation and, if required, certification of a management system. The standards to be respected during an audit are defined in the specific requirements criteria.
The term “audit” is generally understood as a series of control procedures used to assess whether a management system’s processes comply with certain requirements and directives. The aim of the audit is to assess the management system on several levels: compliance with requirements, aptitude of the management system for the operator and effectiveness of the management system in place.
Depending on the scope in question (quality, environment, safety, etc.), the criteria to be met are found in norms, standards or technical specifications.
Audit process
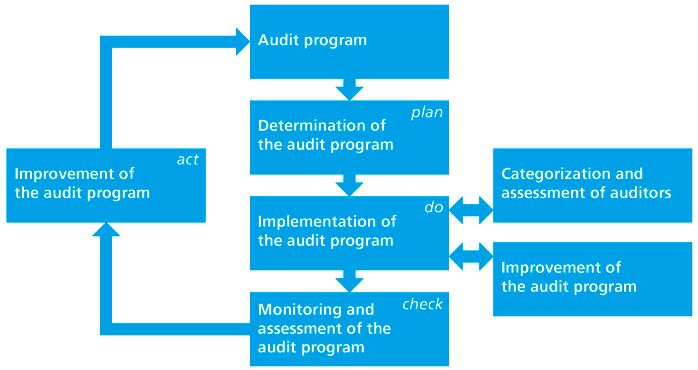
The process for an audit program is presented as follows:
Source: ISO 19011: Guidelines for auditing quality management and/or environmental management systems.
This general process applies to all types of audits. A distinction is made between internal audit and external audit. The internal audit is used to verify that the management system is used correctly and effectively in practice, and that the defined procedures and processes also correspond to current practice. It is also often used as a preparatory stage for certification.
External audit
For an external audit, we differentiate between:
- the second party audit of a supplier or of the company itself as supplier
- the third party audit in the context of granting or monitoring certification of a management system
There is also a distinction between the following types in terms of objective and scope, whether this involves an internal audit or an external audit:
- System audit. Central question: does the management system meet all requirements?
- Process audit. Is a process capable of meeting the objectives set by the policy and the programs?
- Product audit. For a given product, are all internal and external requirements successfully met?
- Compliance audit. Are all statutory, administrative and contractual requirements met?
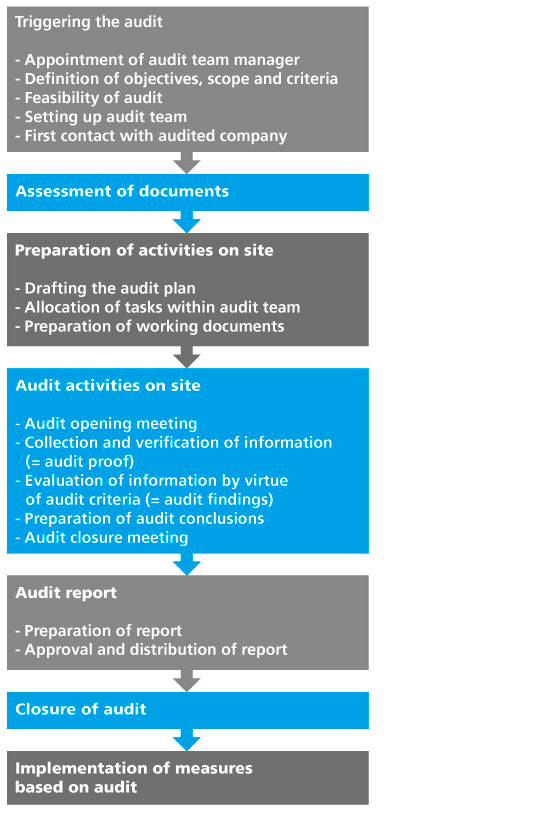
The following points describe typical audit activities:
Source: Umweltmanagement für kleine und mittlere Unternehmen, Hans-Jürgen Klüppel, Beuth, Berlin, 2006.